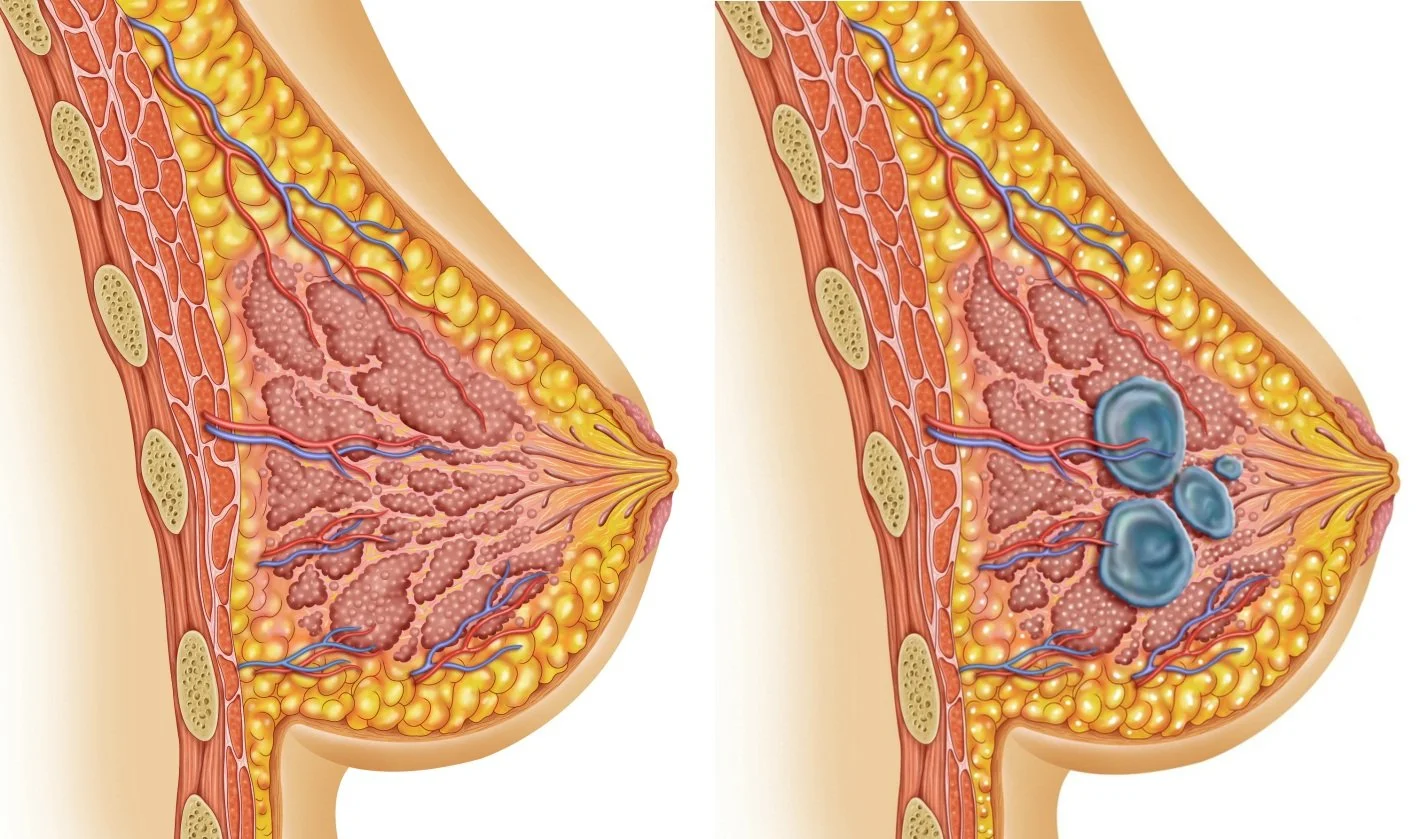
Mastopathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Methods
Mastopathy is a serious diagnosis made for nearly every woman at different periods in her life, and the number of cases has been increasing year by year. It most frequently affects women of childbearing age from 30 to 50 years old. The main group consists of women suffering from various gynecological diseases, such as painful premenstrual syndrome, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, endocrine infertility, uterine fibroids, and endometriosis. The incidence of breast cancer in this group is 3 to 5 times higher than in healthy women.
Causes of Mastopathy:
The primary cause of mastopathy is an imbalance of female sex hormones. Dysregulation of the nervous control of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, ovaries, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland leads to hormonal disruption. The neurohumoral factor also plays a role, where nervous system disorders, such as psychoses and neuroses, can trigger the disease. Risk factors include liver and thyroid gland diseases.
Symptoms of Mastopathy:
The initial stage of the disease manifests with breast pain that intensifies a few days before menstruation begins. The pain can vary in character and intensity. As the disease progresses, the pain becomes more intense and prolonged. Upon palpation, nodules and painful areas may be found in the breast.
Treatment Methods:
Diagnosis includes examination, palpation, and instrumental methods such as mammography. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medication, dietary recommendations, and physical activity. In some cases, surgical intervention may be required.
Herbal Treatment for Mastopathy
Treatment principles for mastopathy are defined by a systemic approach, encompassing a variety of factors leading to the disease and considering the characteristics of hormonal status, metabolism, and personal traits of the patient.
Herbal treatment for mastopathy involves a comprehensive approach. The initial stage aims to normalize disrupted neurohumoral regulation. Subsequent steps support body regulation at a physiological level. Effective herbal treatment also includes addressing coexisting conditions such as ovarian dysfunction, liver issues, cholecystitis, thyrotoxicosis, and diabetes, which are often causes of mastopathy.
It's important to note that mechanisms regulating genital pathology also operate in the mammary glands. Therefore, isolating mastopathy and gynecological pathology is a mistake. Treatment of mastopathy should include correction of coexisting pathology and hormonal status.
Thus, phytotherapy for mastopathy includes the following directions:
Main:
1. Normalization of endocrine relationships.
2. Direct impact on the tumor.
3. Immunomodulation.
Supportive:
1. Treatment of thyroid gland diseases.
2. Regulation and stabilization of metabolic processes in the body.
3. Treatment of liver and gallbladder diseases.
4. Elimination of venous congestion in the pelvis.
5. Elimination of colon dysbiosis syndrome.
6. Sedative Herbal therapy.
7. Active elimination of toxins from the body.
8. Replenishment of vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Herbal treatment represents an effective and safe method for women who prefer natural health approaches. It is crucial to consult with a doctor before starting any treatment, including herbal remedies, to avoid potential side effects and ensure optimal results.
Mastopathy and Hirudotherapy (Leech Therapy)
Hirudotherapy shows high effectiveness in treating mastopathy! A leech is essentially a biofactory that produces saliva containing many biologically active substances. Among them are hirudin (a blood-thinning agent) and a multitude of superenzymes that have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-edema effects, and regulate hormonal levels.
Since the basis of mastopathy is always a hormonal imbalance, associated organs and systems are also affected. This disease often accompanies various gynecological conditions, such as dysfunctional ovarian disorders, endometriosis, ovarian and cervical cysts, uterine polyps, fibroids, and endometrial hyperplasia. It's important to consider this coexisting pathology when treating mastopathy and apply a comprehensive approach aimed at eliminating the cause.
The combination of phytotherapy and hirudotherapy provides a holistic impact on the body, improving metabolism, regenerative processes, and normalizing hormonal levels. Hirudotherapy helps eliminate congestion in organs and tissues, normalizing blood and lymph circulation in the breast, reducing nodular formations, and improving skin and subcutaneous tissue structure.
In treating mastopathy, leeches are usually applied both on the affected breast and on biologically active points corresponding to the meridian. The treatment course is determined based on the patient's medical history and visual examination, and personal health characteristics.
Hirudotherapy is an effective method for treating mastopathy, improving patient conditions and reducing disease symptoms.
Conclusion:
Mastopathy is a serious disease that requires careful medical observation and a comprehensive approach to treatment. Timely diagnosis and proper treatment can help prevent complications and improve the quality